Retinoid receptors
Retinoic acid (RA) is a hydrophobic ligand. Its
receptor exists in the nucleus.
Functional receptor is a heterodimer consisting of
two closely similar proteins
named retinoic acid receptor (RAR) and retinoid X receptor
(RXR). The genes for
these two proteins belong to the nuclear receptor superfamily.
In vertebrates,
the nuclear receptors have been well characterized.
The heterodimer binds specific
DNA sequences and activates transcription of its target
genes depending on ligand.
We isolated RAR and RXR cDNA clones from Polyandrocarpa
misakiensis. This
is the first report of invertebrate RAR. We demonstrated
that the Polyandrocarpa
RAR/RXR can bind specific DNA sequences (Figure) and
activate a reporter gene
transcription depending on RA.

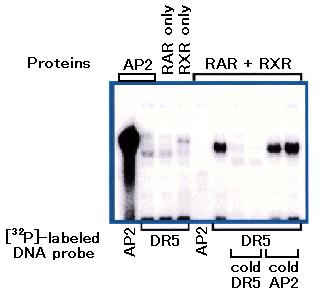
Figure: Electrophoretic mobility shift assay demonstrating that the ascidian
RAR/RXR complex binds to a specific DNA sequence. DR5 oligonucleotide probe
contains a strong binding site for vertebrate RAR/RXR heterodimers. AP2
probe
contains a specific binding site for a transcription factor AP2. AP2 protein
binds
to AP2 probe but not to DR5 probe. The mixture of ascidian RAR and RXR can
bind to DR5 probe but not to AP2 probe. When either RAR or RXR only were
added to the binding reaction, electrophoretic mobility of DR5 DNA did not
shift,
suggesting that RAR and RXR bind to the DR5 sequence as a heterodimer.
References
Hisata, K., Fujiwara, S., Tsuchida, Y., Ohashi, M.
& Kawamura, K. (1998)
Expression and function of a retinoic acid receptor
in budding ascidians.
Develop. Genes Evol. 208: 537-546.
Kamimura, M., Fujiwara, S., Kawamura, K. & Yubisui,
T. (2000) Functional
retinoid receptors in budding ascidians. Dev.
Growth Differ. 42: 1-8.
Fujiwara, S., Kamimura, M., Ohashi, M. & Kawamura,
K. (2001) Molecular bases
of bud development in ascidians. In The Biology
of Ascidians. (ed. Sawada, H.,
Lambert,C. & Yokosawa,H.) Elsevier Science Publisher,
pp.300-304.